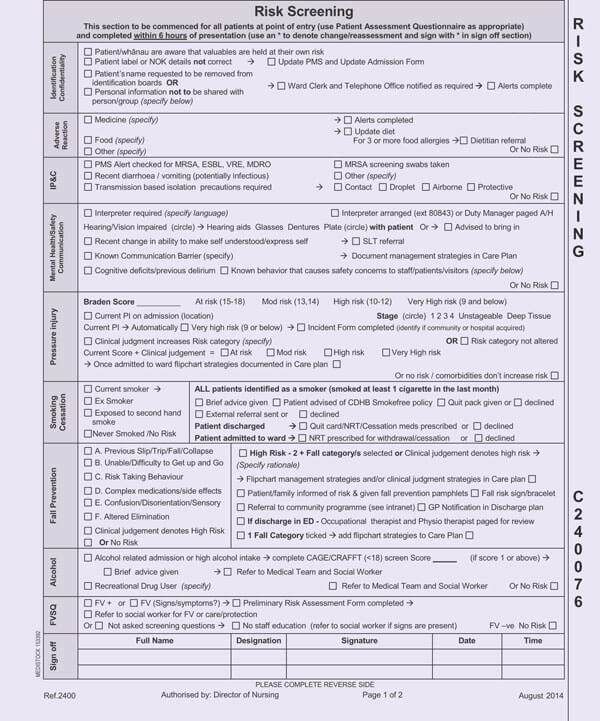
Nursing assessment is one of the best skills that any nurse should possess. This simple skill can help you run your operations much smoother and also help you eliminate any preventable surprises in your day. As a nurse, assessment is a great way of learning about your patient’s concerns, symptoms, and overall health.
What is the Nursing Assessment?
Nursing assessment is gathering a patient’s data, including their psychological, physiological, sociological, and spiritual status, by a registered nurse. This is usually the first step in the nursing process. For instance, if a patient is hospitalized, the nurse will conduct their first assessment of the patient, including their manifestation of pain and their response to other basic elements to help them determine the best way to handle the patient.
Types of Nursing Assessments
Initial Assessment:
This is also referred to as triage. It helps in determining the nature of the problem and helps prepare the patient for other assessment stages. The initial assessment is usually thorough compared to other assessments and may include putting the patient through a physical exam and assessing their mental health.
Focused Assessment:
This is the stage in which the patient’s problem is exposed and treated accordingly. During this assessment, vital signs are continuously monitored and depending on the initial treatment for pain that the patient is under. The root cause is continuously monitored, and the necessary treatment is done.
Time-Lapsed Assessment:
Once the root cause of the pain has been identified and treated, a time-lapsed assessment is then conducted to ensure that the patient is recovering and their condition is stabilizing. During this assessment, the patient’s condition is compared to their previous baseline and before the treatment.
Emergency Assessments:
When a patient has to undergo an emergency procedure, the nurse’s focus is usually on rapid identification of the root causes of a patient’s pain, assessing their airway and their breathing and air circulation. Once all these components have been stabilized, the emergency assessment may turn into an initial or focused assessment depending on the patient’s situation.
How to Prepare the Assessment
Start by preparing a systematic approach to how you are going to assess the patient. You can use the head-to-toe approach, starting with the head and next and slowly progressing down to the body and examining the feet last.
After preparing the assessment approach that you are going to use to assess the patient, prepare yourself, the environment, and the patient.
When preparing yourself, make sure that all the examination equipment is ready and that you have mastered the examination techniques. Some of the equipment to include in your checklist include:
- Gloves
- Watch
- Blood pressure cuff
- Thermometer
- Otoscope
- Tongue depressor
- Ophthalmoscope
- Sterile sharp object
- Reflex hammer Etc.
NOTE: all the equipment needed for the assessment should be clean, in good working condition, and readily accessible.
When preparing the environment, you want to make sure that the room is warm enough for the patient and that the patient’s family/friends are not present in the room.
Five Steps of a Nursing Process
Basically, there are five steps of the nursing process. The processes are in place to ensure that patient care is comprehensive and well organized. Although all the steps have a unique purpose, they are all interdependent, and they all require information from the other to develop a comprehensive plan of care for the patient. The nursing process involves:
Assessment Phase:
This is the first phase of the nursing process. During this phase, the patient’s data is gathered, including their psychological, physiological, sociological, and spiritual status, by a registered nurse. The nurse can use various ways to collect this data, including conducting physical exams, obtaining the patient’s medical records, or by general observation of the patient’s response.
Diagnosis Phase:
This second phase of the nursing process involves the nurse using their skills and judgment to diagnose a current or potential health condition of the patient. These diagnoses are also used to determine their readiness for any health improvements and whether or not they are at risk of affecting others. This phase is usually very critical as it determines the patient’s course of treatment.
Planning Phase:
The planning phase is where the goals and outcomes are formulated. This phase can only commence once the nurse, the doctors, and the patient agree on the diagnosis. If the patient has more complicated conditions such as a syndrome or has suffered multiple injuries, the senior nurse must prioritize the diagnoses and focus more on the most urgent and crucial conditions.
Implementing Phase:
The implementation phase involves initiating interventions and treatments to help the patient realize the set goals and desired outcomes. The implementation phase can take place over the course of days, hours, weeks, or even months. This phase may involve monitoring the patient for any signs of change or improvement, instructing the patient about their health management, and contacting the patient to follow up on their condition.
Evaluation Phase:
This is the last stage of the nursing process. This phase is set to determine whether the goals and outcomes of the assessment have been met. The possible patient outcomes are usually categorized into three: Improved, Stabilized, and deteriorated/died or discharged.
If the patient’s condition has shown no sign of improvement or if the goals set are not realized, then the nursing process begins again from the first step.
Psycho-social Assessment
A psychosocial assessment is an assessment of a patient’s mental health condition and their social well-being. Psycho social assessment involves:
- Assessment of the patient’s cognitive functions
- Checking if the patient is experiencing hallucination or delusions
- Evaluation of their concentration levels and;
- Inquiring about their interests and the different activities that affect their mental and emotional health.
Cultural Assessment
Cultural assessment is usually conducted to help in identifying key factors that may hamper the implementation of nursing diagnosis and care. The information obtained during this assessment should include:
- The patient’s religious practices
- Their living arrangements
- Their ethnicity, language, and need for an interpreter
- The language that they prefer for both written and verbal instructions
Physical Assessments
Here are important things that you should know about when conducting a physical assessment:
- Physical assessments can take a lot of time depending on the nature of the exam
- Physical assessments can either be passive observation, hands-on or both
- When conducting the physical assessment, you should be systematic and thorough
- When conducting the physical assessment, ensure that the patient’s privacy is considered and they are comfortable during the assessment
- Ensure that your hands are warm when conducting the test for the patient’s comfort
- Ensure that your fingers are short and neat to avoid injuring the patient during the assessment
What is the Head-to-Toe Assessment Sequence?
The head-to-toe assessment is an all-inclusive process that reviews the health of all the major body systems, from our head down to our toes.
The head-to-toe sequence is as follows:
- General status: Check on the general appearance of the patient
- Head, ears, Eyes, Nose, and Throat: start your assessment on the patient’s head. Check to see if there are any abnormalities
- Neck: Is the patients’ neck, ok? Are there are worrying signs? Does the patient have any signs of goiter or any other disease or infection?
- Respiratory: Is the patient’s lung sounds, ok? As the patient about their coughing
- Cardiac: Check on the patient’s heartbeat
- Abdomen: Inspect the patient’s abdomen and ask them if they have any problems with their bladder or bowel
- Pulses: check the patient’s pulses in their arms, leg, and feet, including their radial, femoral, and dorsalis pedis
- Extremities: assess the patient’s range of strength and motion in their legs, arms, and ankles
- Skin: check to see if the patient’s skin is dry, cold, flushed, or hot or if they have any tenderness, lesions, or lumps
- Neurological: examine the patient’s coordination, their reflexes, and assess their gait. Also, check on their Glasgow Coma Scale score
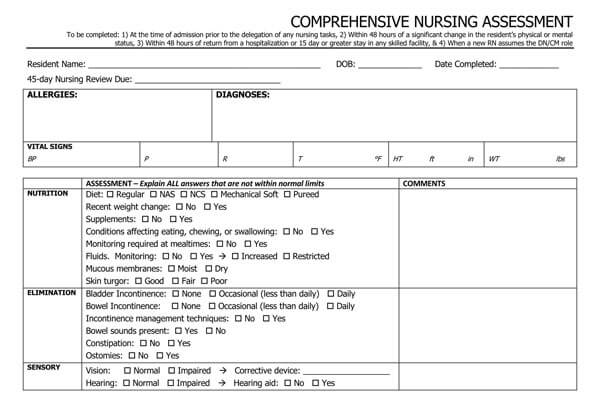
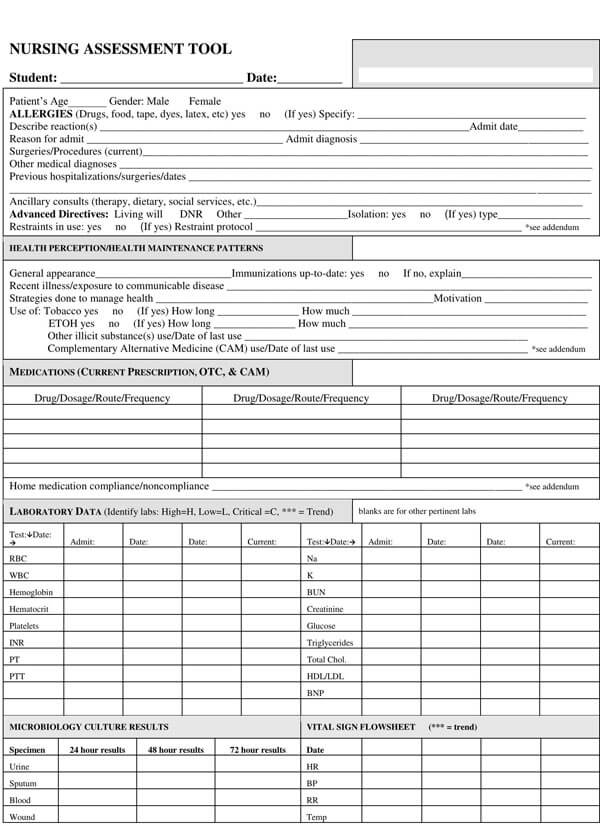
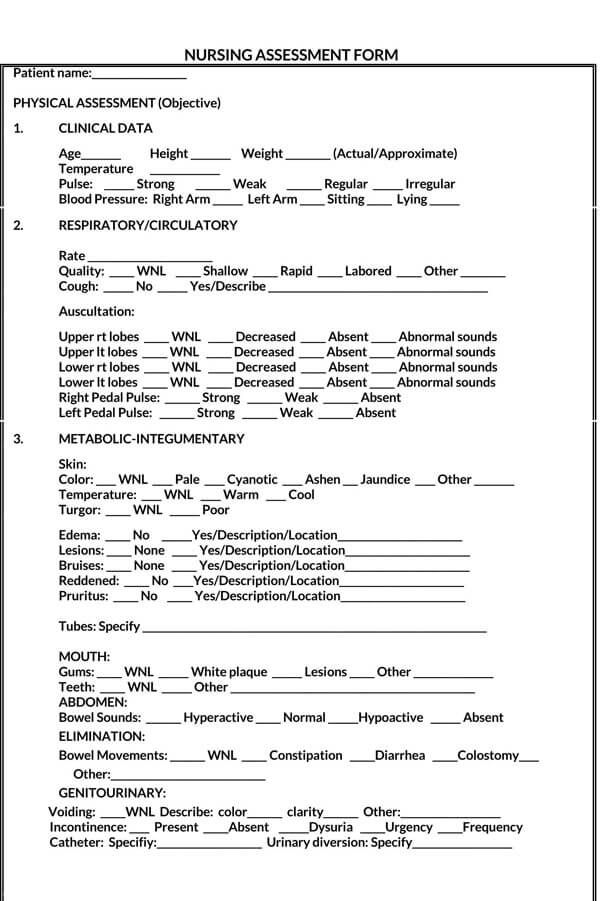
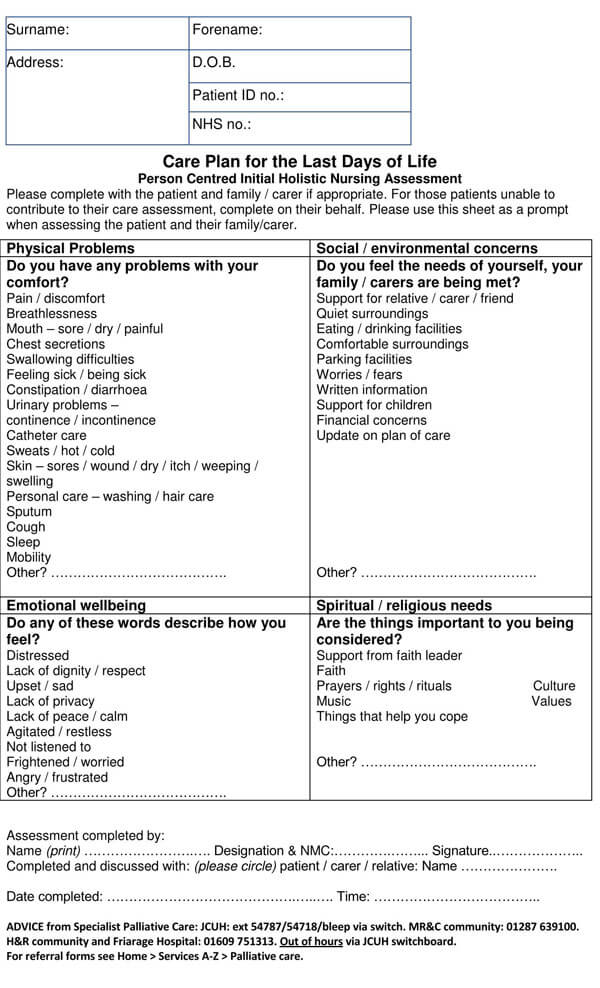
Nursing Assessment Examples
It is common for people to forget things, especially when they are under pressure. To ensure that you cover all the areas in your assessment, download and use our free and premium nursing assessment templates today to get started on your assessment.
Conclusion
A comprehensive nursing assessment is the first stage of the nursing process. The assessment provides the foundation for care that allows patients to gain a greater enhance their health status and gain greater control over their lives.